Blog by John Dunsmuir
Browser UI Extensions: Establishing Best Practices for a Novel Framework
6 min read

Author: Andy Stevens
5 min read
In my last blog post we looked at using the JConsole to view and invoke WebLogic MBean methods. JConsole is a nice way to get an overview of what WebLogic operations are available but what we really want to do is run some WebLogic tasks automatically! In this post I'll show you how to use Apache Ant (which ships with OBI 11g), and a tiny bit of batch scripting to run WebLogic Scripting Tool (WLST) scripts.
The WLST is designed for automating WebLogic tasks so we'll definitely be using this, but it's a scripting environment and not so much an automation tool. WLST doesn't really help us if we need to do some non-WebLogic tasks, that's where Apache Ant comes in. Ant is a Java based build automation tool which allows you to automate a range of tasks using XML 'build' files to describe the process. In this post we'll use Ant to run a WebLogic script that prints the status of the Oracle BI server, to do this you'll need to create three files.
Fig 1. Files required to run WLST from ANT
File 1 - RunScript.bat
This batch file enables us to set environment variables before making the call to Ant.
File 2 - AntSctipt.xml
This is the Ant build script which will be interacting with WLST. The RunScript.bat file above passes this file as a parameter to Ant.
File 3 - ServerStatus.py
This is the script that will be passed into WLST to print the status of the BI Server to the screen, it contains the Jython-like scripting language that WLST executes.
Now you might be thinking "why not just use a batch script to run WLST directly instead of using Ant?", well, you could do that but here are some of the benefits of using Ant:
If you take a peek into the Start/Stop BI Services icons in the start menu you will see that Ant is already being used to manage the BI Services in windows
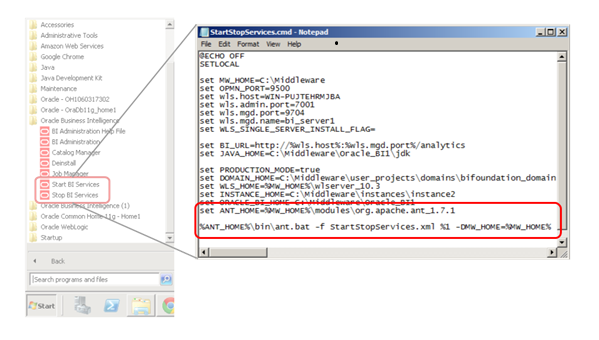 Fig 2. OBIEE uses a pre-installed version of Ant to start and stop the BI Services
Fig 2. OBIEE uses a pre-installed version of Ant to start and stop the BI Services
Okay so let's get into the fun stuff.
Here is a look at the RunScript.bat file, be sure to change the MW_HOME directory path to your own, you shouldn't have to change anything else:
@ECHO OFF
SETLOCAL
set MW_HOME=D:\oracle\obiee
set ANT_HOME=%MW_HOME%\modules\org.apache.ant_1.7.1
set JAVA_HOME=%MW_HOME%\Oracle_BI1\jdk
set weblogic.lib.dir=%MW_HOME%\wlserver_10.3\server\lib
%ANT_HOME%\bin\ant.bat -f AntScript2.xml -lib
%weblogic.lib.dir%\weblogic.jar && pause
As you can see above we are simply setting some environment variables and then executing Ant.bat with the XML build file as a parameter. We also add Oracle's weblogic.jar file to the classpath so that the Ant file knows how to communicate with WLST. Now let's have a look at the AntScript.xml file, if you have had any experience at all with Ant you will have no problem understanding the build script:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="windows-1252" ?>
<project name="Run WLST project" default="run-wlst-script">
<property environment="env"/>
<taskdef name="wlst"
classname="weblogic.ant.taskdefs.management.WLSTTask"/>
<target name="run-wlst-script">
<wlst debug="false" failonerror="true" filename="ServerStatus.py">
</wlst>
</target>
</project>
Basically, this script creates a new task definition called wlst, which we use further down in the script, and provides the name of the class which implements it (weblogic.ant.taskdefs.management.WLSTTask). It then runs the WLST task with the ServerStatus.py script as a parameter, any code in the ServerStatus.py file will then be executed by the WLST. Note that for the sake of simplicity I have hard-coded the location of the ServerStatus.py file but you could pass this in as a parameter.
Okay so next is the ServerStatus.py file, this is where the actual WLST script goes. Make sure you use your own WebLogic username, password and URL instead of mine:
print "Connecting..."
connect('weblogic','welcome1','t3://localhost:7001')
domainCustom()
cd ('oracle.biee.admin')
print 'Connecing to BIInstance MBean'
cd ('oracle.biee.admin:type=BIDomain.BIInstance,biInstance=coreapplication,group=Service')
print 'BIInstance MBean; ServiceStatus: ' + get('ServiceStatus')
print 'Disconnecting...'
exit()
This is quite an easy script to understand if you've had any experience with WebLogic scripting. The script connects to the BI domain, navigates to the oracle.biee.admin MBean and gets the 'ServiceStatus' attribute, printing it out to the screen. Again, for simplicity I've hard-coded the username, password and WebLogic URL here but it would be a good idea to store these in a user-configuration file.
Now that all of the files have been created you can double click on the RunScript.bat file to see the status of the BI Server. Here is a look at the output:
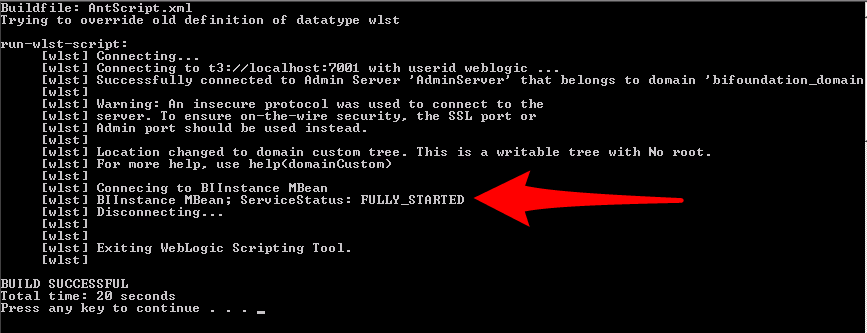
Fig 3. Script output showing the status of the BI Server
Obviously you can do much more than simply printing the status of the BI server to the console - like uploading the BI Repository or bouncing the BI servers etc - but the purpose of this post was just to show you how to use Ant together with WLST. Have fun thinking of things to automate!
Boxfusion Consulting are an Oracle Platinum Partner and are recognised by Oracle as Specialised in the implementation of Oracle BI technology.
If you would like to hear more about how Oracle BI might be used to help your business please contact us.
6 min read
4 min read
The latest version of Siebel has many great architectural features to improve support and ...
2 min read